「数値を ’01’ や ‘0005’ のように表示したいけど、JavaScriptでどうやってゼロ埋めすればいいの?」
そんな悩みをお持ちの方へ向けた記事です。
業務で商品IDや会員番号、日付や時刻を扱う場面では、表示の統一感が求められますよね。見た目を整えるだけでなく、ソートの整合性やシステム間連携の正確性にも関わってくるため、意外と重要な処理です。しかし、JavaScriptには0埋め専用の構文があるわけではなく、初学者の方や普段あまり文字列処理を意識しない方にとっては「どう書けばスマートなのか」がわかりづらいポイントでもあります。
この記事では、基本的なpadStart()の使い方から、slice()やテンプレートリテラルなどを用いた代替手法まで幅広く解説します。
「ちょっとした表示の違い」が、プロジェクト全体の品質につながることもあります。ぜひこの機会に、0埋め処理をしっかり押さえておきましょう。
JavaScriptで0埋めを実現する基本テクニック
JavaScriptにおけるゼロ埋め(0埋め)は、数値や文字列を指定した桁数に揃えるための重要なテクニックです。日付表示や商品ID管理など、フロントエンド開発では頻繁に使用される処理の一つです。

padStart()で簡単ゼロ埋め:2桁・4桁の数値や日付を整形
ES2017(ES8)から導入されたpadStart()メソッドは、現在最も推奨される0埋めの実装方法です。このメソッドは、文字列の先頭に指定した文字を追加して、目標の長さまで文字列を拡張します。

基本的な使い方
// 基本構文:文字列.padStart(目標の長さ, 埋める文字)
const number = '5';
const paddedNumber = number.padStart(3, '0');
console.log(paddedNumber); // "005"
// 1桁を2桁にゼロ埋め
const singleDigit = '7';
console.log(singleDigit.padStart(2, '0')); // "07"
// 数値を4桁にゼロ埋め
const productId = '23';
console.log(productId.padStart(4, '0')); // "0023"
日付や時刻の0埋め処理
日付や時刻の表示において、padStart()は特に威力を発揮します。
// 現在の日付を取得
const now = new Date();
const month = (now.getMonth() + 1).toString().padStart(2, '0'); // 月は0から始まるため+1
const day = now.getDate().toString().padStart(2, '0');
const hours = now.getHours().toString().padStart(2, '0');
const minutes = now.getMinutes().toString().padStart(2, '0');
console.log(`${month}月${day}日 ${hours}:${minutes}`); // "08月05日 14:30" のような形式
// より実用的な日付フォーマット関数
function formatDate(date) {
const year = date.getFullYear();
const month = (date.getMonth() + 1).toString().padStart(2, '0');
const day = date.getDate().toString().padStart(2, '0');
return `${year}-${month}-${day}`;
}
console.log(formatDate(new Date())); // "2024-08-05"
padStart()の注意点と型変換のポイント(数値→文字列)
padStart()メソッドを使用する際の最も重要な注意点は、このメソッドが文字列に対してのみ機能するということです。数値に対して直接使用することはできません。
数値の型変換が必要な理由
// ❌ 数値に対してpadStart()を直接使用するとエラー
const number = 5;
// console.log(number.padStart(2, '0')); // TypeError: number.padStart is not a function
// ✅ toString()で文字列に変換してからpadStart()を使用
const number = 5;
console.log(number.toString().padStart(2, '0')); // "05"
// ✅ String()関数を使用する方法
console.log(String(number).padStart(2, '0')); // "05"
// ✅ テンプレートリテラルを使用する方法
console.log(`${number}`.padStart(2, '0')); // "05"
実際の開発での型変換パターン
// APIから取得したIDが数値の場合
function formatProductId(id) {
// 型の安全性を考慮した実装
const stringId = typeof id === 'number' ? id.toString() : String(id);
return 'P' + stringId.padStart(5, '0');
}
console.log(formatProductId(123)); // "P00123"
console.log(formatProductId('45')); // "P00045"
console.log(formatProductId(null)); // "P00000" (nullは"null"文字列になる)
// より厳密な型チェックを行う場合
function formatProductIdStrict(id) {
if (typeof id !== 'number' && typeof id !== 'string') {
throw new Error('IDは数値または文字列である必要があります');
}
const numericId = typeof id === 'string' ? parseInt(id, 10) : id;
if (isNaN(numericId)) {
throw new Error('有効な数値IDを入力してください');
}
return 'P' + numericId.toString().padStart(5, '0');
}
slice()やテンプレートリテラルを使った0埋めの代替手法と使い分け
padStart()が利用できない古いブラウザ環境や、よりシンプルな実装を求める場合には、従来の手法も有効です。
slice()を使った0埋め
// slice()を使った2桁0埋めの実装
function zeroPadWithSlice(num, digits = 2) {
const zeros = '0'.repeat(digits);
return (zeros + num).slice(-digits);
}
console.log(zeroPadWithSlice(5)); // "05"
console.log(zeroPadWithSlice(123)); // "23" (指定桁数より大きい場合は切り取られる)
// より柔軟な実装
function zeroPadFlexible(num, digits = 2) {
const str = String(num);
if (str.length >= digits) {
return str; // 既に目標桁数以上の場合はそのまま返す
}
return ('0'.repeat(digits) + str).slice(-digits);
}
console.log(zeroPadFlexible(5)); // "05"
console.log(zeroPadFlexible(123)); // "123" (そのまま返される)
文字列連結を使った手法
// シンプルな文字列連結による0埋め
function simpleZeroPad(num) {
return num < 10 ? '0' + num : String(num);
}
console.log(simpleZeroPad(5)); // "05"
console.log(simpleZeroPad(15)); // "15"
// 三項演算子を使った1行での実装
const formatTwoDigits = (num) => num < 10 ? `0${num}` : `${num}`;
// 時刻表示での実用例
const now = new Date();
const timeString = `${formatTwoDigits(now.getHours())}:${formatTwoDigits(now.getMinutes())}`;
console.log(timeString); // "14:05" のような形式
各手法の使い分け指針
padStart()を使うべき場面:
- モダンブラウザ対応のプロジェクト
- 可読性を重視する場合
- 柔軟な桁数指定が必要な場合
従来手法を使うべき場面:
- 古いブラウザサポートが必要
- バンドルサイズを最小限に抑えたい
- 固定の桁数(特に2桁)のみの処理
// ブラウザサポートを考慮した実装例
function universalZeroPad(num, digits = 2) {
const str = String(num);
// padStart()が利用可能かチェック
if (str.padStart) {
return str.padStart(digits, '0');
}
// フォールバック実装
const zeros = '0'.repeat(digits);
return (zeros + str).slice(-digits);
}
console.log(universalZeroPad(7)); // "07"
console.log(universalZeroPad(123, 5)); // "00123"
これらの基本テクニックを理解することで、様々なシチュエーションに応じた適切な0埋め処理を実装できるようになります。次のセクションでは、これらの知識を活用した具体的な実装パターンを詳しく見ていきましょう。
パターン別0埋め実装例
実際の開発現場では、様々なシチュエーションで0埋め処理が必要になります。このセクションでは、よく遭遇する具体的なパターンごとに、実用的な実装例を詳しく解説します。
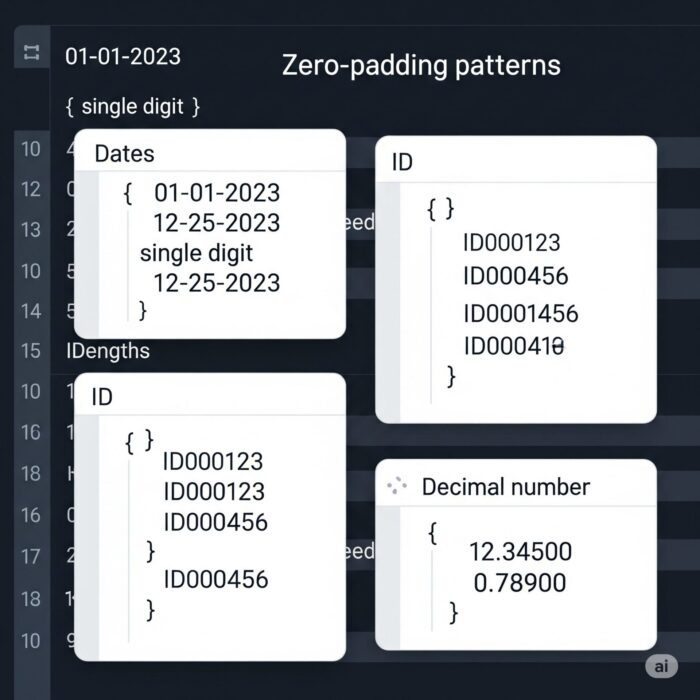
日付フォーマット(YYYY-MM-DD)を常に2桁で表示する
日付の表示は、Webアプリケーションで最も頻繁に使用される0埋め処理の一つです。特に、データベースとの連携やAPIレスポンスの標準化において、統一されたフォーマットが重要になります。
基本的な日付フォーマット関数
// 基本的な日付フォーマット関数
function formatDateBasic(date) {
const year = date.getFullYear();
const month = (date.getMonth() + 1).toString().padStart(2, '0'); // 月は0から始まるため+1
const day = date.getDate().toString().padStart(2, '0');
return `${year}-${month}-${day}`;
}
// 使用例
const today = new Date();
console.log(formatDateBasic(today)); // "2024-08-05"
const specificDate = new Date(2024, 0, 7); // 2024年1月7日
console.log(formatDateBasic(specificDate)); // "2024-01-07"
より高機能な日付フォーマッター
// 様々な日付フォーマットに対応した関数
function formatDate(date, format = 'YYYY-MM-DD') {
const year = date.getFullYear();
const month = (date.getMonth() + 1).toString().padStart(2, '0');
const day = date.getDate().toString().padStart(2, '0');
const hours = date.getHours().toString().padStart(2, '0');
const minutes = date.getMinutes().toString().padStart(2, '0');
const seconds = date.getSeconds().toString().padStart(2, '0');
const formatMap = {
'YYYY-MM-DD': `${year}-${month}-${day}`,
'YYYY/MM/DD': `${year}/${month}/${day}`,
'MM/DD/YYYY': `${month}/${day}/${year}`,
'YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm': `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hours}:${minutes}`,
'YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss': `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hours}:${minutes}:${seconds}`,
'Japanese': `${year}年${month}月${day}日`
};
return formatMap[format] || formatMap['YYYY-MM-DD'];
}
// 使用例
const now = new Date();
console.log(formatDate(now, 'YYYY-MM-DD')); // "2024-08-05"
console.log(formatDate(now, 'YYYY/MM/DD')); // "2024/08/05"
console.log(formatDate(now, 'MM/DD/YYYY')); // "08/05/2024"
console.log(formatDate(now, 'Japanese')); // "2024年08月05日"
console.log(formatDate(now, 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm')); // "2024-08-05 14:30"
日付入力フィールドとの連携
// HTML input[type="date"]との互換性を考慮した実装
class DateFormatter {
static toInputFormat(date) {
// input[type="date"]は YYYY-MM-DD 形式を要求
return formatDate(date, 'YYYY-MM-DD');
}
static fromInputFormat(dateString) {
// "2024-08-05" → Date オブジェクト
const [year, month, day] = dateString.split('-').map(Number);
return new Date(year, month - 1, day); // 月は0から始まるため-1
}
static getCurrentWeek() {
const today = new Date();
const week = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
const date = new Date(today);
date.setDate(today.getDate() + i);
week.push(this.toInputFormat(date));
}
return week;
}
}
// 使用例
console.log(DateFormatter.toInputFormat(new Date())); // "2024-08-05"
console.log(DateFormatter.getCurrentWeek());
// ["2024-08-05", "2024-08-06", "2024-08-07", ...]
商品ID・注文番号など固定長IDをゼロ埋めで整形する
ECサイトや管理システムでは、IDの表示や管理において統一されたフォーマットが重要です。
商品ID生成システム
// 商品IDフォーマッター
class ProductIdFormatter {
constructor(prefix = 'P', totalLength = 6) {
this.prefix = prefix;
this.idLength = totalLength - prefix.length;
}
format(id) {
const numericId = typeof id === 'number' ? id : parseInt(id, 10);
if (isNaN(numericId) || numericId < 0) {
throw new Error('有効な商品IDを入力してください');
}
return this.prefix + numericId.toString().padStart(this.idLength, '0');
}
parse(formattedId) {
if (!formattedId.startsWith(this.prefix)) {
throw new Error(`商品IDは${this.prefix}で始まる必要があります`);
}
const numericPart = formattedId.slice(this.prefix.length);
return parseInt(numericPart, 10);
}
}
// 使用例
const productFormatter = new ProductIdFormatter('P', 6);
console.log(productFormatter.format(1)); // "P00001"
console.log(productFormatter.format(123)); // "P00123"
console.log(productFormatter.format(99999)); // "P99999"
// 注文番号用のフォーマッター
const orderFormatter = new ProductIdFormatter('ORD', 8);
console.log(orderFormatter.format(42)); // "ORD00042"
// IDの解析
console.log(productFormatter.parse('P00123')); // 123
バッチ処理での連番生成
// 連番ID生成器
function generateSequentialIds(startId, count, formatter) {
const ids = [];
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
ids.push(formatter.format(startId + i));
}
return ids;
}
// 使用例:商品登録の一括処理
const productIds = generateSequentialIds(1001, 5, productFormatter);
console.log(productIds);
// ["P01001", "P01002", "P01003", "P01004", "P01005"]
// CSVエクスポート用のフォーマット
function exportProductList(products) {
const formatter = new ProductIdFormatter('SKU', 7);
return products.map(product => ({
id: formatter.format(product.id),
name: product.name,
price: product.price
}));
}
const products = [
{ id: 1, name: '商品A', price: 1000 },
{ id: 42, name: '商品B', price: 2500 }
];
console.log(exportProductList(products));
// [
// { id: "SKU0001", name: "商品A", price: 1000 },
// { id: "SKU0042", name: "商品B", price: 2500 }
// ]
小数点以下の数値(1.5 → 1.50など)を0埋めでフォーマットする
価格表示や計測値の表示において、小数点以下の桁数を統一することは重要です。
価格表示のフォーマット
// 価格フォーマッター
class PriceFormatter {
constructor(decimalPlaces = 2, currency = '¥') {
this.decimalPlaces = decimalPlaces;
this.currency = currency;
}
format(price) {
const numericPrice = typeof price === 'string' ? parseFloat(price) : price;
if (isNaN(numericPrice)) {
throw new Error('有効な価格を入力してください');
}
const formattedPrice = numericPrice.toFixed(this.decimalPlaces);
return `${this.currency}${formattedPrice}`;
}
// 3桁区切りのカンマ付きフォーマット
formatWithCommas(price) {
const formatted = this.format(price);
const [currency, amount] = [formatted.charAt(0), formatted.slice(1)];
const [integer, decimal] = amount.split('.');
const integerWithCommas = integer.replace(/\\B(?=(\\d{3})+(?!\\d))/g, ',');
return `${currency}${integerWithCommas}.${decimal}`;
}
}
// 使用例
const jpyFormatter = new PriceFormatter(2, '¥');
console.log(jpyFormatter.format(1500)); // "¥1500.00"
console.log(jpyFormatter.format(1.5)); // "¥1.50"
console.log(jpyFormatter.format('2.3')); // "¥2.30"
console.log(jpyFormatter.formatWithCommas(1234567.89)); // "¥1,234,567.89"
// USD表示用
const usdFormatter = new PriceFormatter(2, '$');
console.log(usdFormatter.format(19.9)); // "$19.90"
測定値・統計値のフォーマット
// 科学計算や統計表示用のフォーマッター
class NumericFormatter {
static formatDecimal(value, decimalPlaces = 2) {
return parseFloat(value).toFixed(decimalPlaces);
}
static formatPercentage(value, decimalPlaces = 1) {
return `${(value * 100).toFixed(decimalPlaces)}%`;
}
static formatMeasurement(value, unit = '', decimalPlaces = 2) {
const formatted = parseFloat(value).toFixed(decimalPlaces);
return unit ? `${formatted}${unit}` : formatted;
}
// 統計データの整形
static formatStats(stats) {
return {
average: this.formatDecimal(stats.average),
min: this.formatDecimal(stats.min),
max: this.formatDecimal(stats.max),
standardDeviation: this.formatDecimal(stats.standardDeviation, 3)
};
}
}
// 使用例
console.log(NumericFormatter.formatDecimal(3.14159, 3)); // "3.142"
console.log(NumericFormatter.formatPercentage(0.847)); // "84.7%"
console.log(NumericFormatter.formatMeasurement(25.7, 'kg', 1)); // "25.7kg"
const statsData = {
average: 12.345,
min: 8.1,
max: 18.99,
standardDeviation: 3.14159
};
console.log(NumericFormatter.formatStats(statsData));
// {
// average: "12.35",
// min: "8.10",
// max: "18.99",
// standardDeviation: "3.142"
// }
動的精度調整機能
// 値の大きさに応じて自動的に精度を調整するフォーマッター
class AdaptiveFormatter {
static smartFormat(value, maxDecimalPlaces = 2) {
const num = parseFloat(value);
if (isNaN(num)) return '0.00';
// 整数の場合
if (Number.isInteger(num)) {
return num.toString() + '.00';
}
// 小数点以下の有効桁数を計算
const decimalPart = num.toString().split('.')[1] || '';
const significantDecimals = decimalPart.replace(/0+$/, '').length;
const precision = Math.min(significantDecimals, maxDecimalPlaces);
return num.toFixed(Math.max(precision, 2));
}
// 表示用の単位付きフォーマット
static formatWithUnit(value, unit) {
return `${this.smartFormat(value)} ${unit}`;
}
}
// 使用例
console.log(AdaptiveFormatter.smartFormat(5)); // "5.00"
console.log(AdaptiveFormatter.smartFormat(5.1)); // "5.10"
console.log(AdaptiveFormatter.smartFormat(5.123)); // "5.12" (maxDecimalPlaces=2)
console.log(AdaptiveFormatter.smartFormat(5.100)); // "5.10"
console.log(AdaptiveFormatter.formatWithUnit(72.5, 'kg')); // "72.50 kg"
これらの実装例を参考にすることで、様々なデータ形式に対応した柔軟で実用的な0埋め処理を実現できます。次のセクションでは、これらの基本パターンをさらに発展させた高度な応用テクニックを見ていきましょう。
実践で使える0埋め応用テクニックとユースケース
実際の開発現場では、基本的な0埋め処理に加えて、リアルタイム処理、フレームワークとの連携、データの型安全性など、より高度な要求が発生します。このセクションでは、現場で即戦力となる実践的な応用テクニックを詳しく解説します。
リアルタイム入力に対応した0埋め+バリデーション処理の書き方
ユーザーがフォームに入力する際に、リアルタイムで0埋めとバリデーションを適用することで、UXを向上させることができます。
基本的なリアルタイム0埋め処理
// HTMLフォームでのリアルタイム0埋め処理
class RealTimeFormatter {
constructor(inputElement, options = {}) {
this.input = inputElement;
this.options = {
digits: 4,
prefix: '',
allowNegative: false,
maxValue: null,
minValue: 0,
...options
};
this.init();
}
init() {
// 入力時のイベントリスナーを設定
this.input.addEventListener('input', (e) => this.handleInput(e));
this.input.addEventListener('blur', (e) => this.handleBlur(e));
this.input.addEventListener('focus', (e) => this.handleFocus(e));
}
handleInput(event) {
const value = event.target.value;
// 数字以外を除去(負号の処理を含む)
const cleaned = this.cleanInput(value);
// バリデーションチェック
const validationResult = this.validate(cleaned);
if (validationResult.isValid) {
event.target.classList.remove('error');
this.clearErrorMessage();
} else {
event.target.classList.add('error');
this.showErrorMessage(validationResult.message);
}
// 値を更新
event.target.value = cleaned;
}
handleBlur(event) {
const value = event.target.value;
if (value && this.validate(value).isValid) {
// フォーカスが外れた時に0埋めを適用
const formatted = this.formatValue(value);
event.target.value = formatted;
}
}
handleFocus(event) {
// フォーカス時は0埋めを解除して編集しやすくする
const value = event.target.value;
if (value.startsWith(this.options.prefix)) {
const numericValue = this.parseValue(value);
event.target.value = numericValue.toString();
}
}
cleanInput(value) {
// 数字と負号以外を除去
let cleaned = value.replace(/[^\\d-]/g, '');
// 負号の処理
if (!this.options.allowNegative) {
cleaned = cleaned.replace(/-/g, '');
} else {
// 負号は先頭のみ許可
const hasNegative = cleaned.startsWith('-');
cleaned = cleaned.replace(/-/g, '');
if (hasNegative) cleaned = '-' + cleaned;
}
return cleaned;
}
validate(value) {
if (!value) {
return { isValid: true, message: '' };
}
const numericValue = parseInt(value, 10);
if (isNaN(numericValue)) {
return { isValid: false, message: '数値を入力してください' };
}
if (this.options.minValue !== null && numericValue < this.options.minValue) {
return { isValid: false, message: `${this.options.minValue}以上の値を入力してください` };
}
if (this.options.maxValue !== null && numericValue > this.options.maxValue) {
return { isValid: false, message: `${this.options.maxValue}以下の値を入力してください` };
}
return { isValid: true, message: '' };
}
formatValue(value) {
const numericValue = parseInt(value, 10);
if (isNaN(numericValue)) return '';
const padded = numericValue.toString().padStart(this.options.digits, '0');
return this.options.prefix + padded;
}
parseValue(formattedValue) {
if (formattedValue.startsWith(this.options.prefix)) {
return parseInt(formattedValue.slice(this.options.prefix.length), 10);
}
return parseInt(formattedValue, 10);
}
showErrorMessage(message) {
let errorDiv = this.input.nextElementSibling;
if (!errorDiv || !errorDiv.classList.contains('error-message')) {
errorDiv = document.createElement('div');
errorDiv.className = 'error-message';
this.input.parentNode.insertBefore(errorDiv, this.input.nextSibling);
}
errorDiv.textContent = message;
}
clearErrorMessage() {
const errorDiv = this.input.nextElementSibling;
if (errorDiv && errorDiv.classList.contains('error-message')) {
errorDiv.remove();
}
}
}
// 使用例
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function() {
// 商品IDフィールド
const productIdInput = document.getElementById('productId');
new RealTimeFormatter(productIdInput, {
digits: 5,
prefix: 'P',
maxValue: 99999,
minValue: 1
});
// 注文番号フィールド
const orderIdInput = document.getElementById('orderId');
new RealTimeFormatter(orderIdInput, {
digits: 6,
prefix: 'ORD',
maxValue: 999999
});
});
より高度なフォームバリデーション
// 複数フィールドの連携バリデーション
class FormValidator {
constructor(formElement) {
this.form = formElement;
this.fields = new Map();
this.init();
}
addField(name, inputElement, formatter, validator = null) {
this.fields.set(name, {
input: inputElement,
formatter: formatter,
validator: validator,
isValid: true
});
// フォーマッターにバリデーション結果の通知機能を追加
const originalValidate = formatter.validate.bind(formatter);
formatter.validate = (value) => {
const result = originalValidate(value);
this.fields.get(name).isValid = result.isValid;
this.updateFormState();
return result;
};
}
updateFormState() {
const allValid = Array.from(this.fields.values()).every(field => field.isValid);
const submitButton = this.form.querySelector('button[type="submit"]');
if (submitButton) {
submitButton.disabled = !allValid;
}
}
getFormData() {
const data = {};
this.fields.forEach((field, name) => {
if (field.formatter.parseValue) {
data[name] = field.formatter.parseValue(field.input.value);
} else {
data[name] = field.input.value;
}
});
return data;
}
init() {
this.form.addEventListener('submit', (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
if (this.isFormValid()) {
console.log('送信データ:', this.getFormData());
// 実際の送信処理をここに実装
}
});
}
isFormValid() {
return Array.from(this.fields.values()).every(field => field.isValid);
}
}
React/VueやTypeScriptでの型安全な0埋め方法
モダンなフレームワークやTypeScriptを使用する場合、型安全性と再利用性を考慮した実装が重要です。
React + TypeScript での実装
// React + TypeScript での型安全な0埋めコンポーネント
import React, { useState, useCallback, useMemo } from 'react';
interface ZeroPadInputProps {
digits: number;
prefix?: string;
value?: number;
onChange?: (value: number | null) => void;
min?: number;
max?: number;
placeholder?: string;
className?: string;
}
const ZeroPadInput: React.FC<ZeroPadInputProps> = ({
digits,
prefix = '',
value,
onChange,
min = 0,
max,
placeholder,
className = ''
}) => {
const [inputValue, setInputValue] = useState<string>('');
const [isFocused, setIsFocused] = useState<boolean>(false);
const [error, setError] = useState<string>('');
// 表示値の計算(メモ化)
const displayValue = useMemo(() => {
if (isFocused) {
return inputValue;
}
if (value !== undefined && value !== null) {
const padded = value.toString().padStart(digits, '0');
return prefix + padded;
}
return '';
}, [value, inputValue, isFocused, digits, prefix]);
// バリデーション関数
const validateInput = useCallback((val: string): string => {
if (!val) return '';
const numericValue = parseInt(val, 10);
if (isNaN(numericValue)) {
return '数値を入力してください';
}
if (numericValue < min) {
return `${min}以上の値を入力してください`;
}
if (max !== undefined && numericValue > max) {
return `${max}以下の値を入力してください`;
}
return '';
}, [min, max]);
const handleInputChange = (e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
const rawValue = e.target.value;
const cleanedValue = rawValue.replace(/[^\\d]/g, '');
setInputValue(cleanedValue);
const errorMessage = validateInput(cleanedValue);
setError(errorMessage);
if (!errorMessage && onChange) {
const numericValue = cleanedValue ? parseInt(cleanedValue, 10) : null;
onChange(numericValue);
}
};
const handleFocus = () => {
setIsFocused(true);
if (value !== undefined && value !== null) {
setInputValue(value.toString());
}
};
const handleBlur = () => {
setIsFocused(false);
setInputValue('');
};
return (
<div className={`zero-pad-input ${className}`}>
<input
type="text"
value={displayValue}
onChange={handleInputChange}
onFocus={handleFocus}
onBlur={handleBlur}
placeholder={placeholder}
className={error ? 'error' : ''}
/>
{error && <span className="error-message">{error}</span>}
</div>
);
};
// 使用例(React コンポーネント内)
const ProductForm: React.FC = () => {
const [productId, setProductId] = useState<number | null>(null);
const [orderNumber, setOrderNumber] = useState<number | null>(null);
return (
<form>
<div>
<label>商品ID:</label>
<ZeroPadInput
digits={5}
prefix="P"
value={productId}
onChange={setProductId}
min={1}
max={99999}
placeholder="商品IDを入力"
/>
</div>
<div>
<label>注文番号:</label>
<ZeroPadInput
digits={6}
prefix="ORD"
value={orderNumber}
onChange={setOrderNumber}
min={1}
max={999999}
placeholder="注文番号を入力"
/>
</div>
</form>
);
};
Vue 3 + TypeScript での実装
// Vue 3 + TypeScript での0埋めコンポーネント
<template>
<div class="zero-pad-input">
<input
:value="displayValue"
@input="handleInput"
@focus="handleFocus"
@blur="handleBlur"
:placeholder="placeholder"
:class="{ error: hasError }"
/>
<span v-if="errorMessage" class="error-message">{{ errorMessage }}</span>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, computed, watch } from 'vue';
interface Props {
modelValue?: number | null;
digits: number;
prefix?: string;
min?: number;
max?: number;
placeholder?: string;
}
interface Emits {
(e: 'update:modelValue', value: number | null): void;
}
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
prefix: '',
min: 0,
placeholder: ''
});
const emit = defineEmits<Emits>();
const inputValue = ref<string>('');
const isFocused = ref<boolean>(false);
const errorMessage = ref<string>('');
const hasError = computed(() => !!errorMessage.value);
const displayValue = computed(() => {
if (isFocused.value) {
return inputValue.value;
}
if (props.modelValue !== undefined && props.modelValue !== null) {
const padded = props.modelValue.toString().padStart(props.digits, '0');
return props.prefix + padded;
}
return '';
});
const validateInput = (val: string): string => {
if (!val) return '';
const numericValue = parseInt(val, 10);
if (isNaN(numericValue)) {
return '数値を入力してください';
}
if (numericValue < props.min) {
return `${props.min}以上の値を入力してください`;
}
if (props.max !== undefined && numericValue > props.max) {
return `${props.max}以下の値を入力してください`;
}
return '';
};
const handleInput = (e: Event) => {
const target = e.target as HTMLInputElement;
const rawValue = target.value;
const cleanedValue = rawValue.replace(/[^\\d]/g, '');
inputValue.value = cleanedValue;
const error = validateInput(cleanedValue);
errorMessage.value = error;
if (!error) {
const numericValue = cleanedValue ? parseInt(cleanedValue, 10) : null;
emit('update:modelValue', numericValue);
}
};
const handleFocus = () => {
isFocused.value = true;
if (props.modelValue !== undefined && props.modelValue !== null) {
inputValue.value = props.modelValue.toString();
}
};
const handleBlur = () => {
isFocused.value = false;
inputValue.value = '';
};
</script>
TypeScript用ユーティリティ型定義
// TypeScript用の型安全な0埋めユーティリティ
type PaddedString<T extends number> = string & { __paddedLength: T };
type NumericString = string & { __isNumeric: true };
interface ZeroPadOptions {
digits: number;
prefix?: string;
suffix?: string;
}
class TypeSafeZeroPadder {
static pad<T extends number>(
value: number | string,
digits: T,
prefix = ''
): PaddedString<T> {
const numStr = typeof value === 'number' ? value.toString() : value;
const padded = numStr.padStart(digits, '0');
return (prefix + padded) as PaddedString<T>;
}
static parse(paddedValue: PaddedString<any>, prefix = ''): number {
const withoutPrefix = paddedValue.startsWith(prefix)
? paddedValue.slice(prefix.length)
: paddedValue;
const parsed = parseInt(withoutPrefix, 10);
if (isNaN(parsed)) {
throw new Error(`Invalid padded value: ${paddedValue}`);
}
return parsed;
}
// ジェネリクスを使用したバリデーター
static createValidator<T extends ZeroPadOptions>(
options: T
): (value: string) => value is PaddedString<T['digits']> {
return (value: string): value is PaddedString<T['digits']> => {
const expectedLength = (options.prefix?.length || 0) + options.digits + (options.suffix?.length || 0);
if (value.length !== expectedLength) return false;
if (options.prefix && !value.startsWith(options.prefix)) return false;
if (options.suffix && !value.endsWith(options.suffix)) return false;
const numericPart = value.slice(
options.prefix?.length || 0,
value.length - (options.suffix?.length || 0)
);
return /^\\d+$/.test(numericPart);
};
}
}
// 使用例
const productId = TypeSafeZeroPadder.pad(123, 5, 'P'); // PaddedString<5>
const parsedId = TypeSafeZeroPadder.parse(productId, 'P'); // number
const validator = TypeSafeZeroPadder.createValidator({ digits: 5, prefix: 'P' });
const isValid = validator('P00123'); // true
0埋めされた値の扱い方・削除・型変換・ソート時の注意点
0埋めされたデータを扱う際は、型変換やソート処理において特別な注意が必要です。
データの正規化と型変換
// 0埋めデータの正規化クラス
class ZeroPadDataHandler {
static normalizeId(paddedId, prefix = '') {
if (typeof paddedId !== 'string') {
return null;
}
// プレフィックスの除去
const withoutPrefix = prefix ? paddedId.replace(prefix, '') : paddedId;
// 先頭の0を除去して数値に変換
const normalized = parseInt(withoutPrefix, 10);
return isNaN(normalized) ? null : normalized;
}
// 配列データの一括正規化
static normalizeArray(paddedArray, prefix = '') {
return paddedArray
.map(item => this.normalizeId(item, prefix))
.filter(item => item !== null);
}
// JSONデータでの0埋めフィールドの処理
static processJsonData(data, zeroPadFields = []) {
const processed = { ...data };
zeroPadFields.forEach(fieldConfig => {
const { field, prefix = '', keepOriginal = false } = fieldConfig;
if (processed[field]) {
const normalizedValue = this.normalizeId(processed[field], prefix);
if (keepOriginal) {
processed[`${field}_normalized`] = normalizedValue;
} else {
processed[field] = normalizedValue;
}
}
});
return processed;
}
}
// 使用例
const paddedIds = ['P00001', 'P00123', 'P01456'];
const normalizedIds = ZeroPadDataHandler.normalizeArray(paddedIds, 'P');
console.log(normalizedIds); // [1, 123, 1456]
const jsonData = {
productId: 'P00042',
orderId: 'ORD000789',
name: '商品A'
};
const processedData = ZeroPadDataHandler.processJsonData(jsonData, [
{ field: 'productId', prefix: 'P' },
{ field: 'orderId', prefix: 'ORD', keepOriginal: true }
]);
console.log(processedData);
// {
// productId: 42,
// orderId: 789,
// orderId_normalized: 789,
// name: '商品A'
// }
ソート処理の実装
// 0埋めデータに対応したソート機能
class ZeroPadSorter {
// 数値ソート(0埋めされた文字列を数値として扱う)
static numericSort(array, field = null, options = {}) {
const {
ascending = true,
prefix = '',
nullsLast = true
} = options;
return [...array].sort((a, b) => {
let valueA = field ? a[field] : a;
let valueB = field ? b[field] : b;
// プレフィックスの除去と数値変換
const numA = ZeroPadDataHandler.normalizeId(valueA, prefix);
const numB = ZeroPadDataHandler.normalizeId(valueB, prefix);
// null値の処理
if (numA === null && numB === null) return 0;
if (numA === null) return nullsLast ? 1 : -1;
if (numB === null) return nullsLast ? -1 : 1;
const result = numA - numB;
return ascending ? result : -result;
});
}
// 文字列ソート(0埋めを維持)
static lexicographicSort(array, field = null, ascending = true) {
return [...array].sort((a, b) => {
const valueA = field ? a[field] : a;
const valueB = field ? b[field] : b;
const result = valueA.localeCompare(valueB);
return ascending ? result : -result;
});
}
// 混在データのソート(数値と文字列が混在している場合)
static mixedSort(array, field = null, options = {}) {
const { ascending = true, prefix = '' } = options;
return [...array].sort((a, b) => {
let valueA = field ? a[field] : a;
let valueB = field ? b[field] : b;
const numA = ZeroPadDataHandler.normalizeId(valueA, prefix);
const numB = ZeroPadDataHandler.normalizeId(valueB, prefix);
// 両方が数値の場合
if (numA !== null && numB !== null) {
return ascending ? numA - numB : numB - numA;
}
// 文字列として比較
const result = String(valueA).localeCompare(String(valueB));
return ascending ? result : -result;
});
}
}
// 使用例
const products = [
{ id: 'P00010', name: '商品J' },
{ id: 'P00002', name: '商品B' },
{ id: 'P00100', name: '商品Z' },
{ id: 'P00001', name: '商品A' }
];
// 数値ソート(IDを数値として扱う)
const numericSorted = ZeroPadSorter.numericSort(products, 'id', { prefix: 'P' });
console.log('数値ソート:', numericSorted.map(p => p.id));
// ['P00001', 'P00002', 'P00010', 'P00100']
// 文字列ソート(辞書順)
const lexicographicSorted = ZeroPadSorter.lexicographicSort(products, 'id');
console.log('文字列ソート:', lexicographicSorted.map(p => p.id));
// ['P00001', 'P00002', 'P00010', 'P00100']
// 文字列の場合の問題例(0埋めなし)
const problematicIds = ['P10', 'P2', 'P100', 'P1'];
const wrongSort = problematicIds.sort();
console.log('問題のあるソート:', wrongSort);
// ['P1', 'P10', 'P100', 'P2'] - 期待した順序ではない
const correctSort = ZeroPadSorter.numericSort(problematicIds, null, { prefix: 'P' });
console.log('正しいソート:', correctSort);
// ['P1', 'P2', 'P10', 'P100']
データベースとの連携考慮事項
// データベース連携時の0埋めデータハンドリング
class DatabaseZeroPadHandler {
// クエリパラメータの準備
static prepareQueryParams(data, zeroPadFields) {
const prepared = { ...data };
zeroPadFields.forEach(({ field, digits, prefix = '' }) => {
if (prepared[field] !== undefined) {
// データベース保存用の正規化(数値)
prepared[`${field}_numeric`] = ZeroPadDataHandler.normalizeId(prepared[field], prefix);
// 表示用の0埋め形式を保持
prepared[`${field}_formatted`] = prepared[field];
}
});
return prepared;
}
// レスポンスデータの整形
static formatResponse(dbResults, zeroPadFields) {
return dbResults.map(record => {
const formatted = { ...record };
zeroPadFields.forEach(({ field, digits, prefix = '' }) => {
if (record[field] !== undefined) {
// 数値から0埋め形式に変換
formatted[field] = prefix + String(record[field]).padStart(digits, '0');
}
});
return formatted;
});
}
}
// 使用例(Express.js風の実装)
const zeroPadConfig = [
{ field: 'productId', digits: 5, prefix: 'P' },
{ field: 'orderId', digits: 6, prefix: 'ORD' }
];
// POST リクエストのデータ処理
function handleCreateProduct(req, res) {
const processedData = DatabaseZeroPadHandler.prepareQueryParams(
req.body,
zeroPadConfig
);
// データベースに保存(数値として)
// const result = await db.products.create({
// id: processedData.productId_numeric,
// name: processedData.name
// });
console.log('処理されたデータ:', processedData);
}
// GET レスポンスのデータ整形
function handleGetProducts(req, res) {
// const dbResults = await db.products.findAll();
const mockDbResults = [
{ id: 1, name: '商品A' },
{ id: 123, name: '商品B' }
];
const formattedResults = DatabaseZeroPadHandler.formatResponse(
mockDbResults.map(r => ({ productId: r.id, name: r.name })),
zeroPadConfig
);
console.log('整形されたレスポンス:', formattedResults);
// [
// { productId: 'P00001', name: '商品A' },
// { productId: 'P00123', name: '商品B' }
// ]
}
これらの応用テクニックを活用することで、実際のプロダクション環境でも安全で効率的な0埋め処理を実装することができます。特に型安全性とパフォーマンスの両立、そしてデータの整合性の確保が重要なポイントとなります。
よくある質問(FAQ)
-
0埋めのためにライブラリ(
moment.jsなど)を使うべきか? -
基本的にはブラウザ標準のメソッドを活用することを推奨します。
現在の多くのケースでは、JavaScriptの標準メソッドである
padStart()やtoFixed()で十分対応できます。ライブラリの導入は以下の場合に検討しましょう:// 標準メソッドで十分なケース const formatNumber = (num) => num.toString().padStart(3, '0'); console.log(formatNumber(5)); // "005" // ライブラリが有効なケース:複雑な日付処理が多い場合 // import { format } from 'date-fns'; // const formatted = format(new Date(), 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss');ライブラリを検討すべき場合:
- 複雑な日付フォーマットが多数必要
- 国際化対応(多言語・多地域)が必要
- チームで統一されたフォーマット規則が必要
ただし、
moment.jsは現在メンテナンスモードのため、新規プロジェクトではdate-fnsやdayjsなどの軽量な代替ライブラリを検討してください。 【2025年最新】Day.jsの使い方完全マスターガイド - Moment.js比較から実践テクニックまでJavaScript開発者必見!2KBの軽量ライブラリ「Day.js」の使い方を徹底解説。Moment.jsからの移行メリット、基本的な日付取得・フォーマット変更から、加算・減算・比較操作まで実践的なコード例付きで紹介。さらにReact/Node.js環境での活用法、locale設定、タイムゾーン処理のコツまでカバー。初心者から上級者まで使える日付操作テクニックが全て分かる完全ガイドです。
【2025年最新】Day.jsの使い方完全マスターガイド - Moment.js比較から実践テクニックまでJavaScript開発者必見!2KBの軽量ライブラリ「Day.js」の使い方を徹底解説。Moment.jsからの移行メリット、基本的な日付取得・フォーマット変更から、加算・減算・比較操作まで実践的なコード例付きで紹介。さらにReact/Node.js環境での活用法、locale設定、タイムゾーン処理のコツまでカバー。初心者から上級者まで使える日付操作テクニックが全て分かる完全ガイドです。
-
0埋めを右側(末尾)に行う方法は?
-
右側の0埋めには
padEnd()メソッドを使用します。padStart()が文字列の左側(先頭)に文字を追加するのに対し、padEnd()は右側(末尾)に文字を追加します:// 左側0埋め(padStart)
console.log('5'.padStart(3, '0')); // "005"
// 右側0埋め(padEnd)
console.log('5'.padEnd(3, '0')); // "500"
// 小数点以下を0埋めする場合
function formatDecimal(num, decimals) {
const str = num.toString();
const dotIndex = str.indexOf('.');
if (dotIndex === -1) {
// 整数の場合、小数点と0を追加
return str + '.' + '0'.repeat(decimals);
} else {
// 小数点以下を指定桁数まで0埋め
const currentDecimals = str.length - dotIndex - 1;
return str + '0'.repeat(Math.max(0, decimals - currentDecimals));
}
}
console.log(formatDecimal(1.5, 3)); // "1.500"
console.log(formatDecimal(2, 2)); // "2.00"
// よりシンプルにはtoFixed()を使用
console.log((1.5).toFixed(3)); // "1.500"
console.log((2).toFixed(2)); // "2.00"
-
数値型の0埋めされた文字列を元の数値に戻すには?
-
parseInt()、parseFloat()、またはNumber()を使用して型変換します。// 0埋めされた文字列から数値への変換 const paddedString = "005"; const originalNumber = parseInt(paddedString, 10); // 5 console.log(originalNumber); // 5 console.log(typeof originalNumber); // "number" // 小数点がある場合 const paddedDecimal = "01.50"; const originalDecimal = parseFloat(paddedDecimal); // 1.5 console.log(originalDecimal); // 1.5 // Number()でも変換可能 console.log(Number("007")); // 7 console.log(Number("01.50")); // 1.5 // 配列での一括変換例 const paddedNumbers = ["001", "005", "010", "025"]; const originalNumbers = paddedNumbers.map(str => parseInt(str, 10)); console.log(originalNumbers); // [1, 5, 10, 25]注意点:
parseInt()を使用する際は、必ず第2引数に基数(10進数なら10)を指定することで、予期しない変換エラーを防げます。
-
0埋めされた文字列をソートする際の注意点は?
-
文字列としてソートすると数値順にならないため、数値に変換してからソートするか、適切な比較関数を使用します。
// 問題のあるソート例(文字列としてソート)
const paddedStrings = ["010", "002", "100", "020"];
console.log(paddedStrings.sort()); // ["002", "010", "020", "100"] ← 正しい
// しかし、0埋めしていない文字列だと問題が発生
const mixedStrings = ["10", "2", "100", "20"];
console.log(mixedStrings.sort()); // ["10", "100", "2", "20"] ← 文字列順
// 解決策1: 数値に変換してソート
const numbersForSort = ["10", "2", "100", "20"];
numbersForSort.sort((a, b) => Number(a) - Number(b));
console.log(numbersForSort); // ["2", "10", "20", "100"]
// 解決策2: 統一された桁数でゼロ埋めしてから文字列ソート
function standardizeAndSort(numbers) {
const maxLength = Math.max(...numbers.map(n => n.toString().length));
return numbers
.map(n => n.toString().padStart(maxLength, '0'))
.sort()
.map(s => parseInt(s, 10));
}
console.log(standardizeAndSort([10, 2, 100, 20])); // [2, 10, 20, 100]
-
パフォーマンスを重視する場合の0埋め方法は?
-
大量のデータを処理する場合は、
padStart()よりもシンプルな文字列操作の方が高速になることがあります。// 高速な0埋め関数(固定桁数の場合) function fastZeroPad3(num) { return num < 10 ? '00' + num : num < 100 ? '0' + num : '' + num; } // より汎用的だが少し重い方法 function zeroPad(num, length) { return ('0'.repeat(length) + num).slice(-length); } // padStart()を使った標準的な方法 function standardZeroPad(num, length) { return num.toString().padStart(length, '0'); } // パフォーマンス比較が必要な場合は実際に測定 console.time('fastZeroPad3'); for (let i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { fastZeroPad3(i); } console.timeEnd('fastZeroPad3');ただし、通常のアプリケーションでは可読性と保守性を優先し、
padStart()を使用することを推奨します。パフォーマンスが重要な場合のみ、実際のベンチマークを取って最適化を検討してください。
まとめ
JavaScriptでのゼロ埋め(0埋め)について、基本的なpadStart()メソッドから実践的な応用まで幅広く解説してきました。この記事を通して、日付フォーマットや商品ID整形など、実際の開発現場で求められるスキルを身につけていただけたでしょうか。
最も重要なのは、モダンなブラウザではpadStart()が標準的な解決方法だということです。'1'.padStart(2, '0')のようなシンプルな書き方で、確実に0埋めを実現できます。ただし、数値を扱う際は必ずtoString()で文字列に変換してから使用することを忘れずに。
古いブラウザ環境や特殊な要件がある場合は、slice()やテンプレートリテラルを使った代替手法も選択肢として持っておくと安心ですね。特に('00' + value).slice(-2)のような書き方は、コンパクトで分かりやすく、多くの開発者に愛用されています。
実践では、リアルタイム入力対応やバリデーション処理と組み合わせることで、ユーザビリティの高いアプリケーションが作れます。特にフォーム入力で数値を扱う場面では、この記事で学んだテクニックが直接活かされるはずです。
また、0埋めされた文字列をソートする際は、必ず数値に変換してから処理することも覚えておいてください。文字列のまま並べ替えると、"10"が"2"より前に来てしまう問題が発生します。
この記事で紹介した手法は、フロントエンド開発の基礎スキルとして非常に重要です。さらにスキルアップを目指すなら、date-fnsやDay.jsといった専門ライブラリの学習や、Intl.DateTimeFormatを使った国際化対応なども検討してみてください。
JavaScriptの0埋め処理は、見た目はシンプルでも奥が深い技術です。実際のプロジェクトで積極的に使って、経験値を積んでいくことが何より大切ですね。
あわせて読みたい